About This Service
HOW IT WORKS

Step 1: Order
Order your monitoring service online and have a collection kit delivered to your door
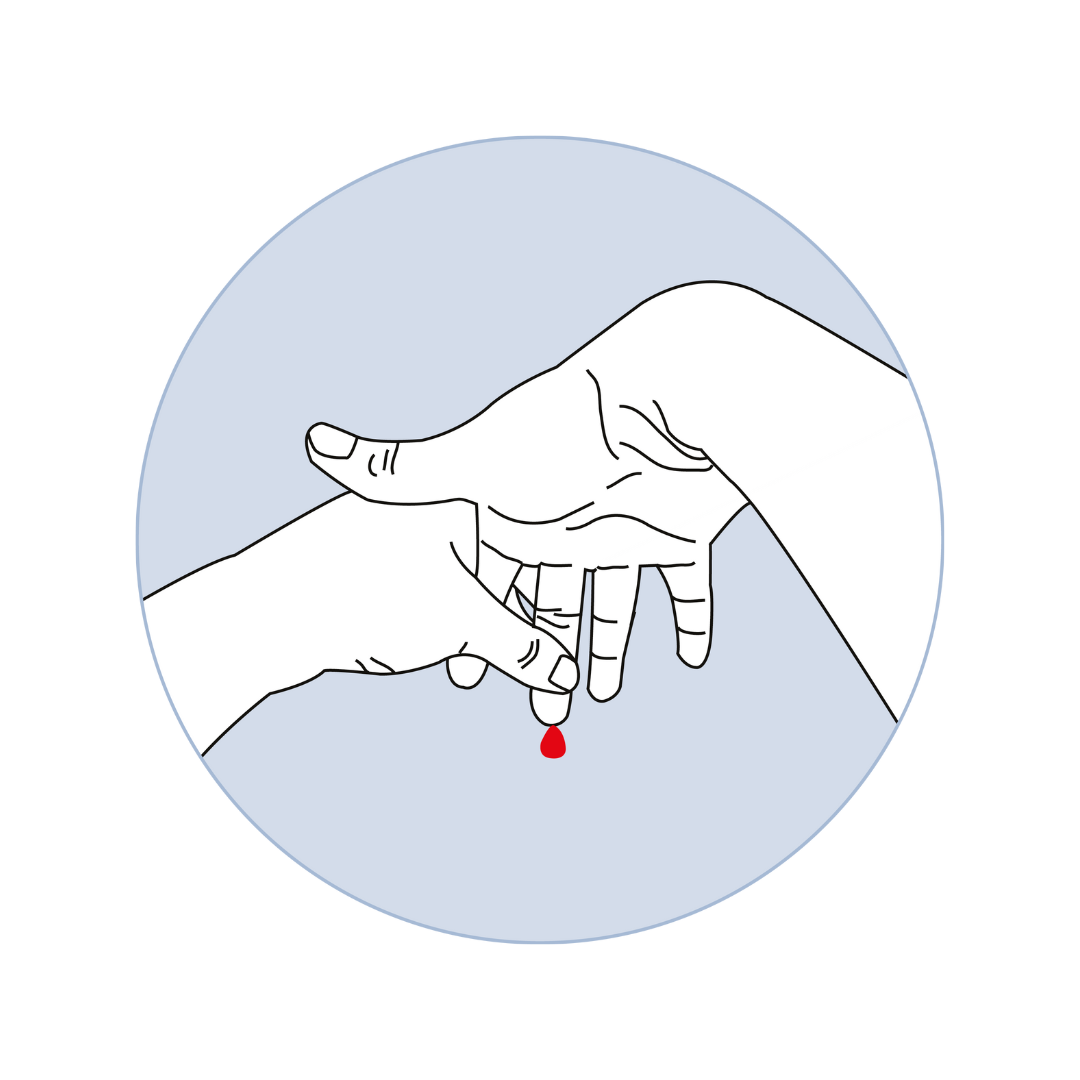
Step 2: Collect & Return
Collect a simple fingerprick blood sample and mail it back reply-paid to our lab. Our quality controlled, accredited Australian laboratory will process your sample.
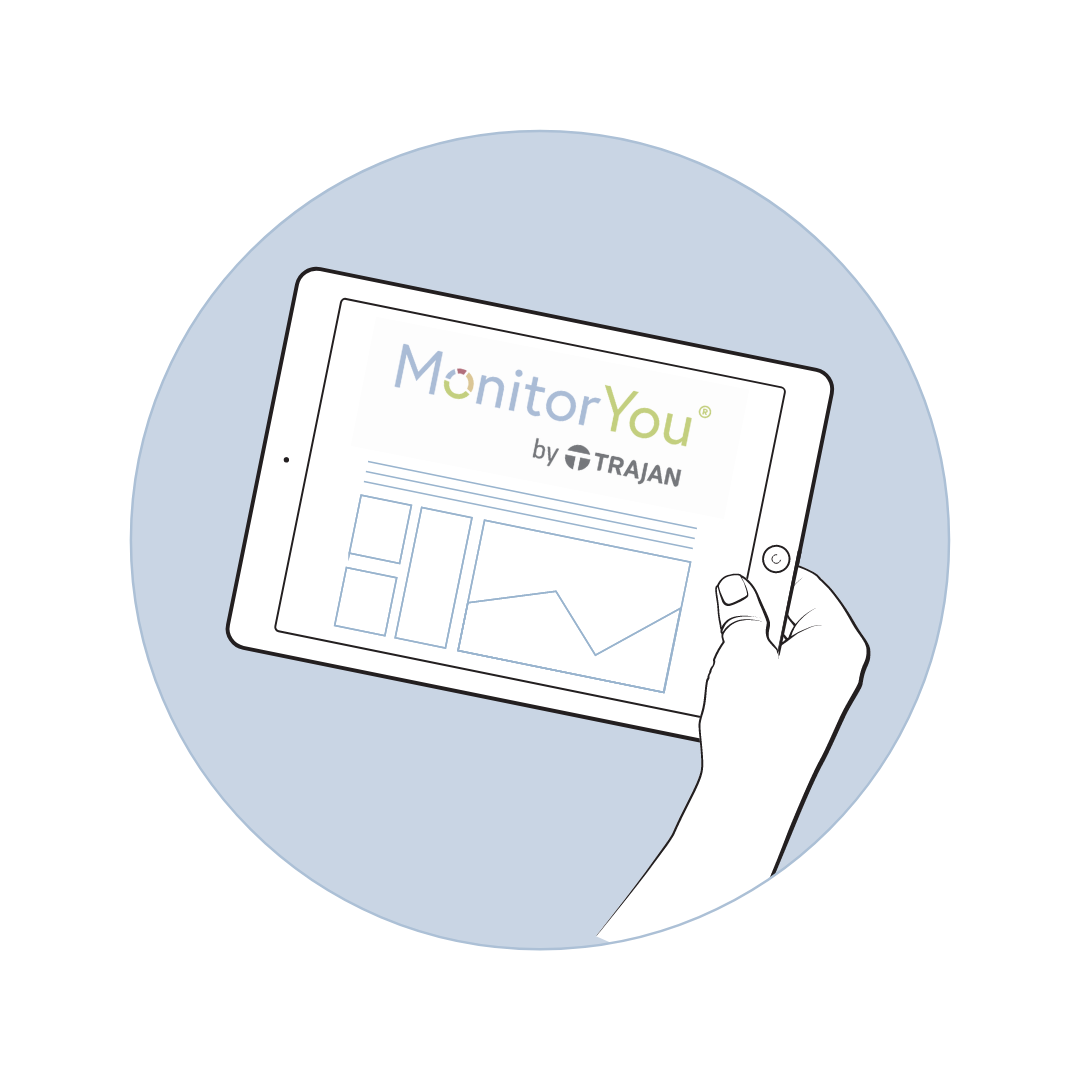
Step 3: View your results
Your results will be delivered via our secured website
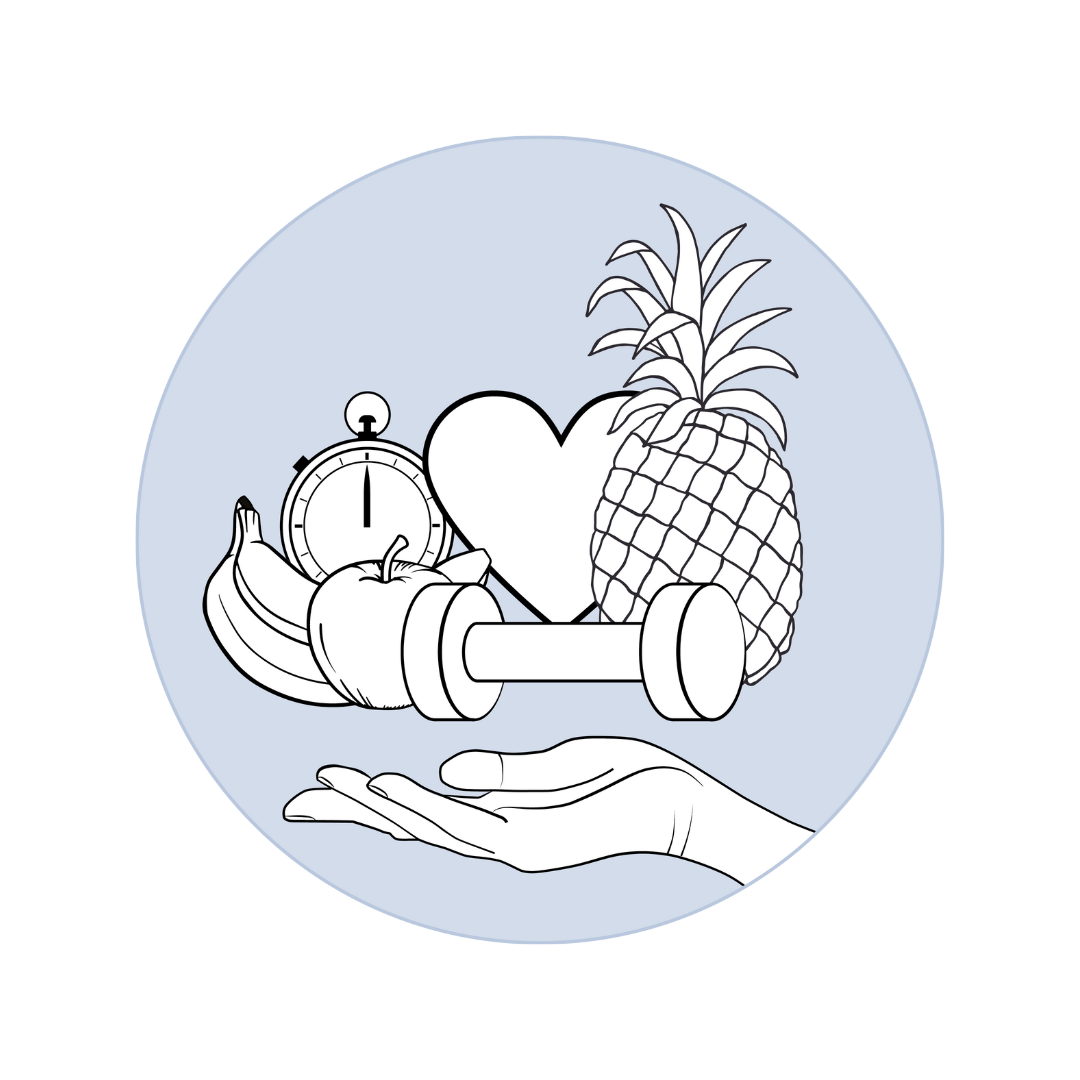

Step 4: Lifestyle Improvements
Make positive changes to your diet and lifestyle to improve your health and continue to track with MonitorYou
Order your monitoring service online and have a collection kit delivered to your door
Collect a simple fingerprick blood sample and mail it back reply-paid to our lab. Our quality controlled Australian laboratory will process your sample.
Your results will be delivered via our secured website
Make positive changes to your diet and lifestyle to improve your health and continue to track with MonitorYou
About Heart Health
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in Australia for both men and women. The term 'heart disease' is often used interchangeably with the term 'cardiovascular disease'. Cardiovascular disease applies to many different diseases typically involving narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Coronary heart disease is the most common type of cardiovascular disease. It is when coronary arteries that supply the heart with blood become hardened and narrow because of a build-up of fatty deposits called plaques.
Heart disease commonly occurs together with high blood pressure, high cholesterol and type 2 diabetes. Many of the risk factors for heart disease have diet and lifestyle habits at their core. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of plant foods high in fibre, being active, not smoking, not drinking too much alcohol, and keeping your body weight in check are all positive lifestyle choices that you can make and are in your control.
Keeping your heart healthy means having a good understanding of your risk factors for heart disease. That will allow you to make the right positive lifestyle choices to reduce your chances of developing heart disease. But the risk of heart disease is something that can slowly build up over time. For this reason, regular health checks with your doctor are important when it comes to heart health, especially if you have a higher risk from such things as a personal or family history of heart disease.
Many of the risk factors for heart disease can be monitored and tracked by looking at changes in different biomarkers in the blood. These biomarkers are strongly linked to the risk of heart disease. The good news is that these biomarkers can respond favourably to lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of heart health biomarkers will allow you to take preventive measures now to lower your risk of developing heart disease in the future.
Cardiovascular Disease
Australian Facts
Some key facts on cardiovascular disease (CVD)

One in four deaths in Australia each year is from CVD

CVD kills 40 percent more males than females
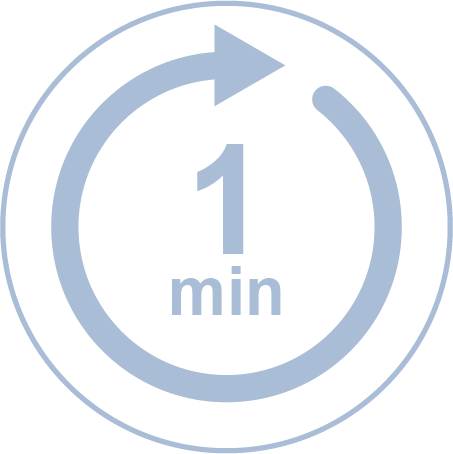
Every minute, someone is hospitalised because of CVD
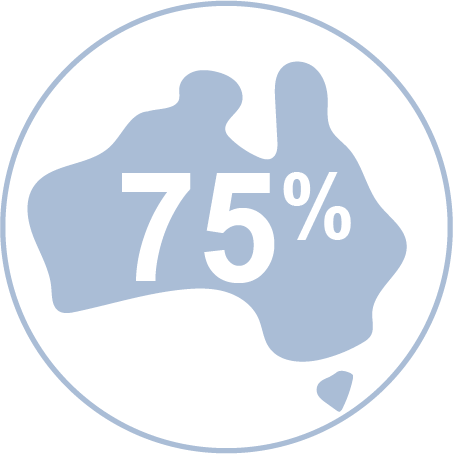

Three-quarters of Australians are at risk of developing CVD

Many risk factors for cardiovascular disease are changeable through a healthy lifestyle.
What is Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a general umbrella term for conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels leading to heart attack, stroke and many other problems. It is the leading cause of death worldwide in men and women.
Heart disease is the most common kind of CVD and happens when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart is reduced or blocked. This can cause angina (chest pain) and heart attack. It can also cause heart failure which occurs when the heart cannot adequately pump blood around the body
Stroke is another common type of CVD. Unlike heart disease where the blood supply to the heart is obstructed, in stroke, the blood supply to the brain is blocked or reduced. The result is the brain is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, causing brain cells to die within minutes.
If the blockage or narrowing of the blood supply to peripheral parts of the body such as the legs happens, then this is called peripheral arterial disease. This can cause a dull cramping pain in the legs which gets worse with walking, muscle weakness, a feeling of numbness and coldness in the legs, and non-healing ulcers on the feet and legs.
There are many causes of CVD, but the most common one related to heart attacks, stroke and peripheral artery disease is explained by a build-up of fatty deposits (called plaque) in the arteries. The presence of these deposits is called atherosclerosis. It can put a person at major risk of blood clots. High blood pressure, smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise and many other factors put a person at a higher risk of CVD.
Signs and symptoms
For coronary heart disease, common signs and symptoms include:
- Chest pain and a feeling of chest tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nausea and sweating
For stroke, the common signs and symptoms include:
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Sudden speech difficulty and weakness of the face muscles
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness and trouble walking
- Sudden severe headache
The warning signs of a heart attack or stroke vary, and it is important to recognise them, as ignoring them could be fatal. Knowing the symptoms and acting on them quickly can increase chance of survival. If you, or someone else, is experiencing the symptoms of a heart attack or stroke, call Triple Zero (000) immediately and ask for an ambulance.
Are you at risk?
Cardiovascular disease is rarely explained by just one risk factor. Often, a combination of related risk factors occurs together to increase a person’s risk. Common risk factors include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Family history of heart disease
- Drinking too much alcohol
- A poor diet low in plant foods and fibre, and high in salt and overly processed sugary and fatty foods
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Not being physically active
- Carrying too much weight, especially around the abdominal area
The Australian Heart Foundation has developed the ‘Heart Age Calculator’. It is a simple way to check your risk of developing heart disease.
Answer these 13 short questions to get your estimated heart age. Your risk of a heart attack or stroke may be higher if your heart age is greater than your actual age.
For more information about heart health, visit the Australian Heart Foundation.
How to maintain a healthy heart
Keeping your heart healthy may be well within your control. That’s because many of the risk factors for heart disease have diet and lifestyle habits at their centre.
The cornerstone of a healthy heart rests with what you eat. And here, it is not about any single food or nutrient, but instead a dietary pattern or theme with lots of scope to tailor it to your food tastes. One of the best known and well-researched heart-healthy dietary patterns is the Mediterranean diet. Common themes of a heart-healthy diet include:
- Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables in place of more highly processed convenience and snack foods
- Making smart swaps by choosing wholegrain foods over more highly refined grains. Choose wholegrain bread over white bread, swap white rice for brown rice or popular grains like quinoa, and choose foods where wholegrains are listed high up in the ingredient list
- Opting for healthier fats like those found in nuts, seeds, salmon, avocados and olive oil
- Including more healthy omega-3 fats in your diet like those found naturally in oily fish, seafood and plant sources such as walnuts, chia, hemp and flaxseed
- Eating less red meat by swapping it for chicken or fish. Or maybe even some of the many varieties of plant powerhouse legumes such as lentils, kidney beans, chickpeas or even tofu
- Adding more spices and herbs to your food instead of salt
Getting more active is one of the most potent health habits that anyone could do. Regular physical activity not only cuts the risk of heart disease, but also the risk of type 2 diabetes and many forms of cancer. It also strengthens your muscles and bones and improves your mental mood. Aim for 30 minutes per day on most days of the week. But just moving more naturally throughout your day will reap benefits.
If you smoke, now is the best time ever to quit or to start the process of smoking less. Smokers are 2-4 times more at risk of developing heart disease compared to non-smokers. The benefits of quitting start almost straight away.
Excess weight is linked to the risk of heart disease. But it is not a case of how much fat you have, but where it is found that is more the issue. It is the dangerous belly fat around the abdomen that you want to have less of. Being more active and eating better will go a long way to helping trim the waistline.
Diabetes
Australian Facts:

1 in 6 people has pre-diabetes
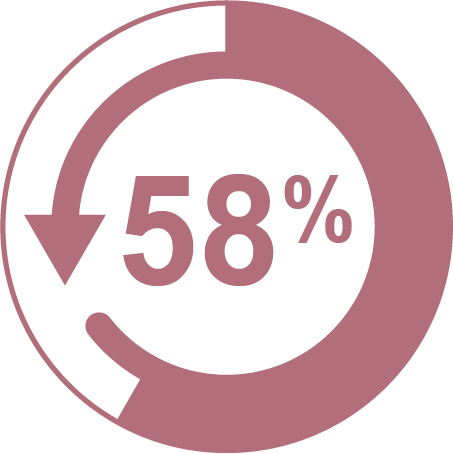

58% of type 2 diabetes cases can be prevented or delayed
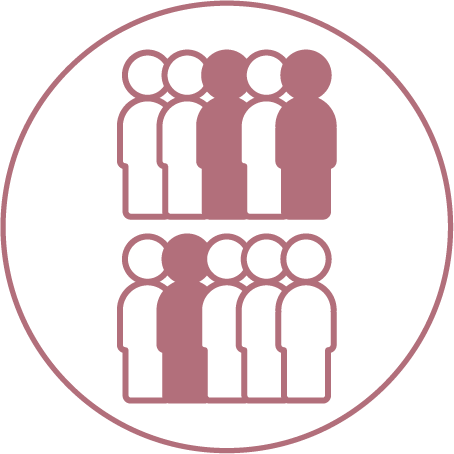

3 in 10 adults with diabetes don’t know it yet
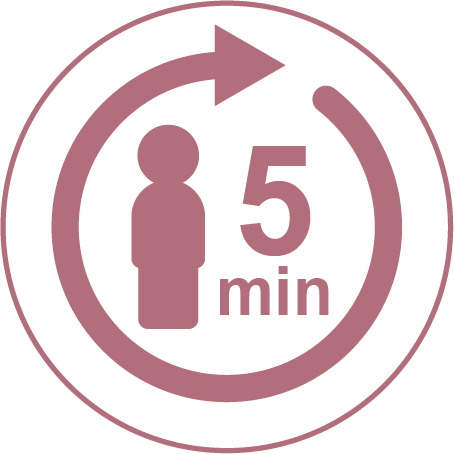

1 person every 5 mins develops diabetes
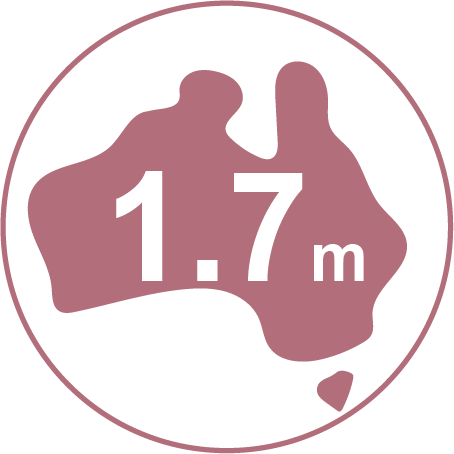

Approx. 1.7 million Australians have diabetes
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where your body is unable to process blood sugar (also known as blood glucose) effectively, causing your blood sugar levels to be too high. High blood sugar levels left untreated can cause damage to your blood vessels, causing serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, hearing loss and lower limb amputations.
There are four main types of diabetes:
Pre-diabetes: where blood sugar levels are higher than the healthy range, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Pre-diabetes affects nearly 1 in 6 adults (more than 2 million individuals) over the age of 25 years. People with pre-diabetes have no symptoms but are at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes, stroke and heart attack. For more info
Type 1 diabetes: this is usually an autoimmune condition. There is no cure and it cannot be prevented. Onset of type 1 diabetes occurs abruptly with obvious symptoms. If you suspect you may have type 1 diabetes seek urgent medical attention. For more info
Type 2 diabetes: this condition gradually develops, usually over a period of years. Some risks of developing type 2 diabetes are unavoidable such as family history and ethnic background, but lifestyle choices play a big part. For more info
Gestational diabetes: a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy that puts the mother and unborn child at risk of serious health problems. Also, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes, and their baby are at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. If you suspect you may have gestational diabetes seek urgent medical attention. For more info
Signs and symptoms
Often there are no symptoms if you’re in the early stages of developing diabetes and many people dismiss the signs as simply part of getting older.
Symptoms include:
- excessive thirst
- passing more urine
- tired or lethargic
- always hungry
- cuts that heal slowly
- itching, skin infections
- blurred vision
- mood swings, headaches, dizziness or leg cramps
- gradually gaining weight (type 2)
Note: This information is of a general nature only and should not be substituted for medical advice. Please consult your doctor about your individual medical needs.
Are you at risk?
People are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes if they:
- have a family history of diabetes
- are over 55 years of age
- are over 45 years of age and are overweight or have high blood pressure
- are over 35 year of age and are of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander background or are from Pacific Island, Indian subcontinent or Chinese cultural background
- have given birth to a child over 4.5kgs or had gestational diabetes (GDM) when pregnant
- have polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Diabetes Australia has developed a Risk Calculator based on the Australian type 2 diabetes risk test (AUSDRISK). It is a simple way to check your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Answer these 11 short questions to assess your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Check my risk
For more information about diabetes, visit Diabetes Australia or Health Direct.
How to reduce risk of diabetes
There are different kinds of diabetes, but the most common one is type 2 diabetes. Almost 1 million currently have type 2 diabetes. Many more Australians have the condition of prediabetes. It is at the stage of prediabetes where lifestyle changes have the biggest impact on reducing the risk of going on to develop type 2 diabetes. Changing your lifestyle can be a big step toward diabetes prevention — and it's never too late to start.
Diabetes Australia gives clear recommendations on how type 2 diabetes can be prevented and are summed up as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular physical activity
- Making healthy food choices
- Managing blood pressure
- Managing cholesterol levels
- Not smoking
There is no one way to eat healthy. Instead, there are guiding principles that apply to everyone, but are even more important for people at risk of diabetes. Healthy food choices centre around these key habits:
- Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Choosing wholegrains over highly refined grains
- Eating less red meat by swapping it for chicken or fish. Or maybe even some of the many varieties of legumes such as lentils, kidney beans, chickpeas or even tofu
- Ditching sugary drinks
- Opting for healthier fats like those found in nuts, seeds, salmon, avocado and olive oil
- Cutting down on salt especially from take-away convenience food and snacks
Even a modest amount of weight loss of around 7 percent can lower the risk of developing diabetes. It all adds up. And for physical activity, aiming for at least 30 minutes a day on most days of the week is a great place to start. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, biking or running are all good aerobic workouts.
Because many people are not aware they are at risk of developing diabetes, then regular monitoring of blood markers such as HbA1c helps you to evaluate the impact of lifestyle changes.